RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
Current projects and development stage
-
Power plants
The Rankine cycle or Rankine Vapor Cycle is the process widely used by power plants such as coal-fired power plants or nuclear reactors. In this mechanism, a fuel is used to produce heat within a boiler, converting water into steam which then expands through a turbine producing useful work. This process was developed in 1859 by Scottish engineer William J.M. Rankine. This is a thermodynamic cycle which converts heat into mechanical energy—which usually gets transformed into electricity by electrical generation.
Using our technology we can make it very efficent.
Oh – did I mention we have designed patend pending way to generate biogas directly in our device, making it one of greenest power source in world?
Prototype stage: prototype.
-
Ejector or jet pump air-conditioning
Basically – the heart of all our cooling systems.
Ejector or jet pump refrigeration is a thermally driven technology that has been used for cooling applications for many years. In their present state of development they have a much lower COP than vapour compression systems but offer advantages of simplicity and no moving parts. Their greatest advantage is their capability to produce refrigeration using waste heat or solar energy as a heat source at temperatures above 80°C.
State of Development
The first steam ejector refrigeration system was developed by Maurice Leblanc in 1910 and gained in popularity for air conditioning applications until the development of chlorofluorocarbon refrigerants in the 1930’s and their use in the vapour compression cycle which was much more efficient than alternative thermally driven cycles. Research and development continued however and the ejector technology found applications in many
engineering fields particularly in the chemical and process industries.Systems have been developed with cooling capacities ranging from a few KW to 60,000 kW but despite extensive development effort the COP (Coefficient Of Performance) of the system.
Thanks to our research and tests we have achieved COP 0.8.
Stage of product: Protype stage.
-
Hybrid module for inverter airconditioning systems
An add-on module to existing air conditioning systems that uses solar energy to generate extra cold and relieve the load on the existing air conditioning system. By using the inverter technology combined with our module, the electricity consumption is drastically reduced (by about 80%).
Product stage: proof of concept.
Estimated prototype stage by 11.2019.
-
Hybrid and non-hybrid air-conditioner with solar panels.
Independent air-conditioning systems – using only jet technology or combined with an inverter compressor (standard air-conditioning solution) with hot water generated by sollar collectors
In non-hybrid mode – no compressor – in countries with a lot of sunshine, the electricity consumption is about 1% of the conventional system. By adding photovoltaic panels, the device can be autonomous.Prototype stage: prototype.
-
Refrigerators for medicine
Refrigerator fully powered by solar panels for short and long-term storage of medicines, vaccines, etc. Application e.g. in developing countries.
Prototype stage: prototype.
-
Vending machines
A vending machine requiring 1% electricity – to power the display and the dispensing mechanism which can be powered by sun which can be located in places without electricity.
Prototype stage: proof of concept.
-
Cold rooms
4 years of tests show us that thanks to our technology, even the most demanding vegetables do not lose their capacity. And all this with minimal energy consumption and the use of modern refrigerants.
Product stage: prototype – ready for market.
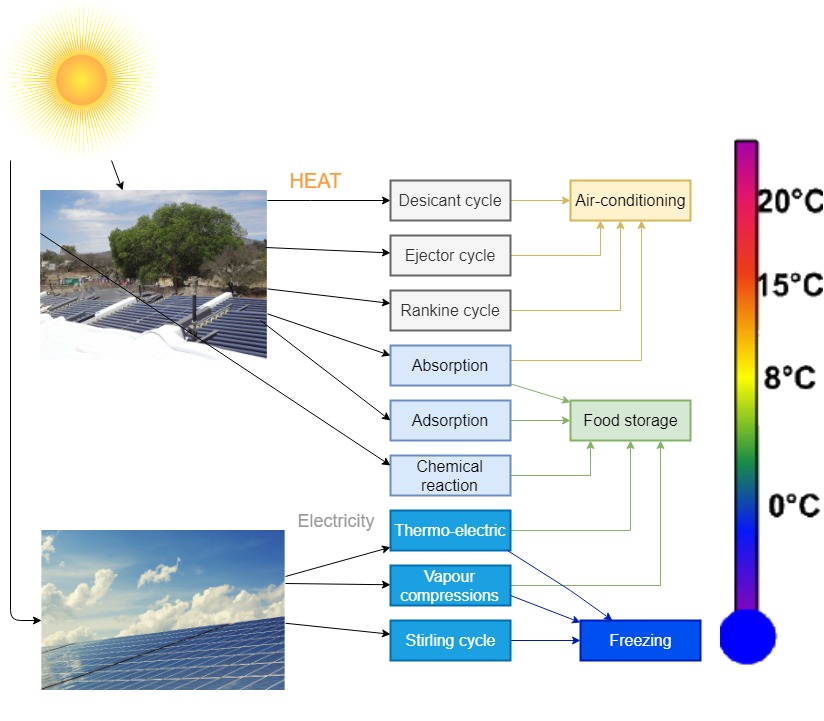
Simplified scheme of solar energy application in HVACR industry